I. Introduction
Organizations that integrate a well-defined purpose into their culture are increasingly demonstrating the potential for both cultural and financial success. Research from Grant Thornton, in collaboration with Oxford Economics, found that companies with extremely healthy cultures are 1.5 times more likely to achieve significant revenue growth (Grant Thornton LLP & Oxford Economics, 2019), underscoring the tangible connection between cultural alignment and financial performance. This finding highlights how a purpose-driven culture fosters an environment where employees feel connected to the organization’s mission, driving both engagement and productivity.
This growing emphasis on purpose reflects a fundamental shift in both workforce and consumer priorities. Employees increasingly seek more than a paycheck; they prioritize roles that align with their personal values and provide opportunities to contribute to something larger than themselves, reflecting a broader move toward purpose-driven work environments (Turner, 2023). Simultaneously, consumers are rewarding brands that demonstrate authenticity and accountability, demanding greater transparency in how companies operate and the impact they have on society (O’Brien, Ouschan, Jarvis, & Soutar, 2020). As these trends converge, businesses are finding that embedding purpose into their culture is not just a moral choice—it is a strategic necessity to remain competitive.
However, purpose alone does not lead to transformation; it must be woven into the organization’s cultural fabric to influence behaviors and decision-making. Culture serves as the mechanism through which values and mission become tangible, shaping the daily actions of employees and leaders alike. This alignment creates a shared sense of identity and trust, inspiring individuals to collaborate, innovate, and contribute their best.
The results of this alignment are far-reaching. Internally, a purpose-driven culture fosters engagement and reduces costly turnover while boosting productivity. Externally, it builds trust with stakeholders, customers, and partners, reinforcing the organization’s reputation and driving loyalty. In a world where differentiation is increasingly challenging, purpose-aligned organizations gain a significant advantage, positioning themselves as leaders in their industries.
By embedding purpose into their culture, businesses can create environments where employees and stakeholders alike thrive. This alignment is no longer an aspirational goal; it is a practical strategy for navigating the complexities of modern markets and achieving sustainable success.
II. Defining Purpose-Driven Transformation
Purpose-driven transformation is a strategic approach that extends beyond the pursuit of profit, aiming to align an organization’s culture and operations with a higher mission that encompasses societal impact, employee well-being, and stakeholder value. It represents a shift in priorities, where businesses strive to create meaningful contributions not only to their bottom line but also to the communities they serve and the individuals within their workforce. In this context, purpose becomes the compass guiding decisions, ensuring that every aspect of the organization reflects its core values and mission.
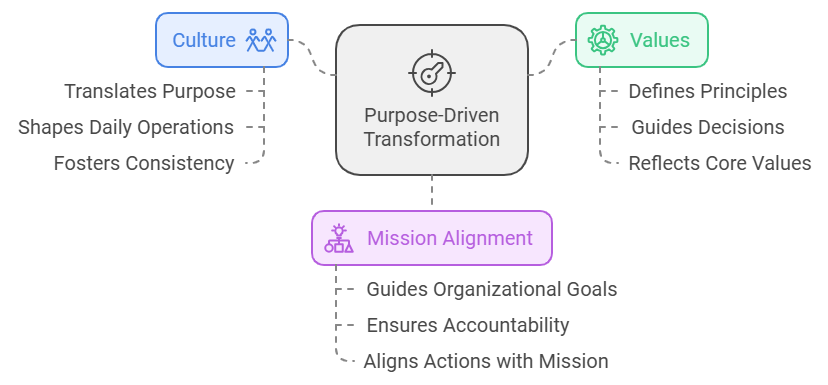
At the heart of purpose-driven transformation are three interconnected elements: culture, values, and mission alignment. These components form the foundation of an organization’s identity and define how it interacts with its employees, customers, and the world at large. Values articulate the principles that the company stands for, while the mission captures its overarching goals and aspirations. Culture, in turn, acts as the living expression of these ideals, shaping how individuals behave, collaborate, and innovate.
Culture plays a pivotal role in translating purpose into actionable outcomes, serving as the foundation for the collective behaviors, norms, and attitudes that shape an organization’s daily operations. When culture is well-aligned with purpose, it ensures that mission statements are not merely aspirational but are reflected in how employees make decisions, engage with stakeholders, and contribute to overarching goals. Acting as a bridge between an organization’s aspirations and its tangible impact, culture enables alignment between values and actions, fostering consistency and accountability throughout the organization (Katzenbach, Oelschlegel, & Thomas, 2016).
When purpose is effectively embedded into culture, it cultivates a cohesive environment where employees gain a clear understanding of not only what they do but also why it matters. This alignment fosters a shared sense of identity and collective commitment, empowering individuals to connect their personal values with the organization’s overarching mission. Additionally, a purpose-driven culture provides clarity and consistency, serving as a steady guide for behavior even amid uncertainty or organizational change (LeaderFactor, 2024).
Without cultural alignment, even the most inspiring mission statements risk becoming empty rhetoric. Culture acts as the conduit that ensures purpose resonates throughout the organization, influencing decisions from the boardroom to the frontlines. By making purpose an integral part of culture, businesses can create a framework for long-term success, balancing profitability with responsibility and making a meaningful difference in the lives of employees, customers, and communities alike.
III. Benefits of Purpose-Driven Transformation
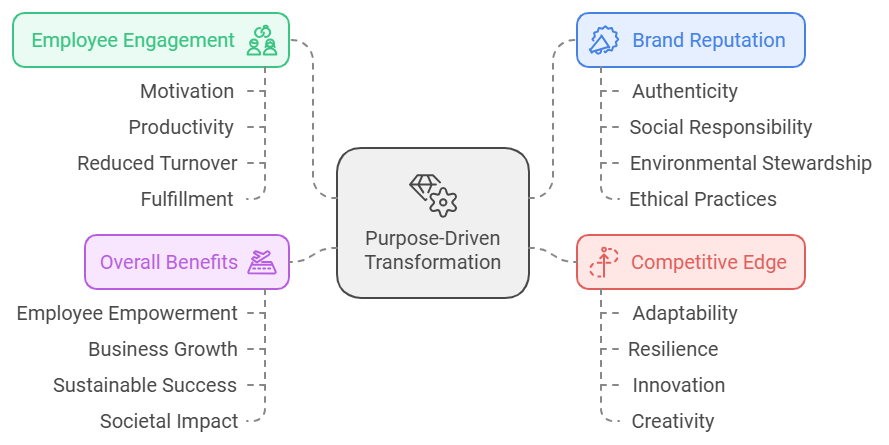
Purpose-driven transformation unlocks a range of benefits that extend beyond the organization itself, driving internal engagement, enhancing external perceptions, and strengthening the ability to compete in a dynamic market. By embedding purpose into culture, businesses create a foundation that supports both individual and collective success.
One of the most significant advantages of purpose-driven transformation is enhanced employee engagement. When employees feel connected to their organization’s mission and purpose, their motivation and commitment improve markedly. This connection fosters a deeper sense of meaning in their roles, making daily tasks more fulfilling and instilling pride in their contributions. Research by Gallup highlights that organizations with engaged employees experience higher productivity, reduced turnover, and better overall performance outcomes, as engaged employees are more likely to stay committed and contribute to their organization’s success (Harter, 2017, 2023). Purpose serves as a psychological anchor, encouraging individuals to invest their energy and creativity in the organization’s goals.
Beyond the workforce, purpose-driven organizations also see significant gains in brand reputation. In an era where consumers and job seekers prioritize authenticity, businesses with a clearly defined purpose stand out as trustworthy and attractive. Customers are increasingly drawn to brands that demonstrate social responsibility, environmental stewardship, and ethical practices, as these values foster trust and meaningful connections between businesses and their audiences (O’Brien et. al., 2020). Simultaneously, top talent gravitates toward organizations whose values mirror their own. Purpose acts as a differentiator, positioning businesses as leaders not just in their industries but in broader societal conversations.
Embedding purpose into culture also delivers a powerful competitive edge. Organizations with a strong sense of purpose are better equipped to navigate challenges and adapt to market shifts. By aligning their values with their mission, these companies foster a culture of resilience and innovation. Employees in purpose-driven environments are more likely to embrace change and approach problems with creativity, as they understand how their efforts contribute to a larger vision. This alignment enables businesses to remain agile and forward-thinking, ensuring they can pivot effectively in response to evolving demands while staying true to their core identity.
The convergence of these benefits—engaged employees, a positive brand image, and a competitive position—illustrates the transformative power of purpose. By integrating values and mission into their culture, organizations can create a sustainable framework for success, empowering both their people and their business to thrive in an ever-changing world.
IV. Steps to Align Organizational Culture with Values and Mission
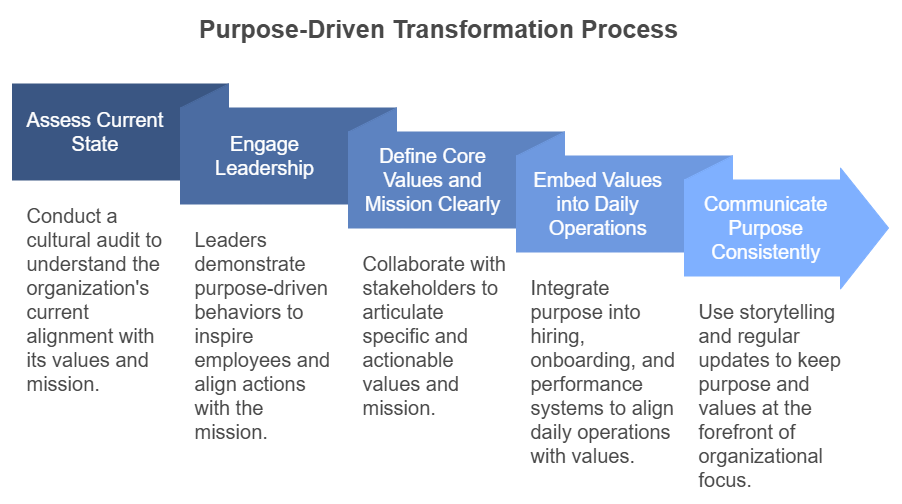
Purpose-driven transformation requires a deliberate and methodical approach to ensure that an organization’s culture authentically reflects its values and mission. By following these steps, businesses can embed purpose into their daily operations, creating an environment where employees and stakeholders feel inspired and connected to a shared vision.
1. Assess the Current State
The first step in aligning culture with values and mission is understanding where the organization currently stands. Conducting a cultural audit can provide valuable insights into whether existing behaviors and attitudes reflect the company’s stated values and mission. Tools such as employee surveys, focus groups, and anonymous feedback platforms can help uncover gaps between the organization’s aspirations and its reality.
This process also involves identifying areas of misalignment. For example, if inclusivity is a core value, yet employees report a lack of diversity in leadership or hiring practices, this disconnect must be addressed. The audit not only serves as a diagnostic tool but also lays the foundation for meaningful change by involving employees in the process, making them feel heard and valued.
2. Engage Leadership
Leadership plays a critical role in embedding purpose into organizational culture. Leaders must not only endorse the mission but also actively demonstrate purpose-driven behaviors in their actions and decisions. Employees look to leadership for cues, and inconsistencies between words and actions can erode trust and undermine the transformation.
Examples of purpose-driven leadership abound. Patagonia’s commitment to environmental activism, championed by its leadership, has been a hallmark of its brand. The company’s CEO and executives model this commitment by advocating for sustainable practices, reinforcing the mission at every level. Leaders who embody purpose set the tone for the organization and inspire employees to follow suit.
3. Define Core Values and Mission Clearly
A clear and authentic mission, coupled with well-defined values, serves as the blueprint for purpose-driven transformation. To ensure relevance, this step should involve collaboration with key stakeholders, including employees, customers, and partners. Their input can help refine the mission to reflect the company’s unique identity and resonate across audiences.
Generic or vague statements should be avoided. Instead, values should be articulated in specific and actionable terms that provide clear guidance on desired behaviors. For example, instead of simply stating “innovation,” a value might emphasize “embracing bold ideas to solve real-world challenges.” A well-crafted mission and set of values serve as a unifying force, guiding the organization toward its goals.
4. Embed Values into Daily Operations
Once values and mission are clearly defined, the next step is to integrate them into everyday business processes. This involves embedding purpose into hiring practices, onboarding programs, performance evaluations, and employee recognition systems.
For instance, Zappos has successfully woven its core value of “delivering happiness” into its operations. From customer service training to employee rewards, the company ensures that its purpose informs how employees interact with customers and one another. Similarly, organizations can design systems that reward behaviors aligning with their mission, reinforcing purpose as a lived experience rather than a distant ideal.
5. Communicate Purpose Consistently
Purpose-driven transformation requires continuous communication to ensure that employees and stakeholders remain aligned. Storytelling is a powerful tool in this regard, enabling leaders to share real examples of how the organization’s mission and values are being realized.
Highlighting success stories, such as a team’s innovative project that exemplifies core values or an employee’s exceptional contribution to the mission, reinforces the importance of purpose. Regularly incorporating purpose into internal communications, such as town halls, newsletters, and team meetings, keeps it top of mind for employees. This consistent reinforcement helps to create a sense of unity and shared ownership of the organization’s goals.
By following these steps, businesses can move beyond aspirational statements and foster a culture where purpose is reflected in every interaction and decision. This alignment not only empowers employees but also strengthens the organization’s ability to thrive in a purpose-driven marketplace.
V. Case Studies: Companies Redefining Culture Through Purpose
Successful purpose-driven transformation often stems from a deep commitment to aligning culture with mission. The following examples demonstrate how companies have redefined their organizational identity through purpose, leading to significant internal and external gains.
Patagonia
Patagonia’s mission, “to save our home planet,” is far more than a slogan—it serves as the guiding principle behind every decision the company makes. This steadfast dedication to environmental sustainability is evident in its supply chain practices, product innovation, and employee policies. Patagonia prioritizes the use of eco-friendly materials, offers repair services to extend the lifecycle of its products, and actively engages in environmental advocacy. Additionally, the company provides employees with paid time off to participate in environmental activism, ensuring that its purpose is reflected at every level of the organization and solidifying its reputation as a purpose-driven brand (Sundheim, 2023).
The results of this alignment are remarkable. Patagonia has cultivated a cult-like following among environmentally conscious consumers and a loyal, motivated workforce. Its leadership in sustainability has set industry standards and elevated the brand as a global advocate for environmental responsibility. By embedding purpose into its culture and operations, Patagonia has demonstrated how an authentic mission can drive business success while making a positive impact on the world.
Microsoft
Under the leadership of CEO Satya Nadella, Microsoft underwent a profound cultural transformation centered on its mission “to empower every person and organization on the planet to achieve more.” This renewed focus on purpose marked a departure from the company’s previous reputation for being overly competitive and hierarchical. Nadella championed empathy, inclusivity, and innovation, fostering a collaborative environment where employees were encouraged to embrace a growth mindset and work together toward shared goals. This cultural shift not only revitalized the organization but also positioned it as a leader in innovation and workplace transformation (Tabrizi, 2023).
One of the most visible changes was Microsoft’s approach to leadership development, which emphasized learning and adaptability over rigid expertise. This cultural realignment enabled the company to embrace new markets, innovate with products like Azure and Teams, and build partnerships once considered unthinkable, such as collaborations with open-source platforms.
The outcomes have been striking. Employee engagement has surged, as reflected in higher satisfaction scores and lower attrition rates. Simultaneously, Microsoft’s stock performance has soared, solidifying its position as one of the world’s most valuable companies. By embedding purpose into its culture, Microsoft has redefined itself as a forward-thinking, people-centered organization.
Ben & Jerry’s
Ben & Jerry’s has consistently demonstrated how social activism can be seamlessly integrated into a successful business model, proving that purpose and profit can coexist. The company’s mission transcends selling ice cream, with a deep commitment to advancing causes such as racial justice, climate action, and fair trade. These values are woven into every aspect of its operations, from sourcing ethically produced ingredients to launching marketing campaigns that amplify its advocacy and engage consumers in meaningful ways (Edmondson, 2013).
This commitment to purpose resonates deeply with consumers, creating a powerful alignment with purpose-driven customers. For example, Ben & Jerry’s has launched flavors that promote social causes, such as “Justice ReMix’d,” which highlights criminal justice reform. Its dedication to activism not only differentiates the brand in a crowded market but also reinforces loyalty among its customer base.
The company’s ability to balance purpose and profitability demonstrates the strength of aligning culture with mission. By making its values a core part of its identity, Ben & Jerry’s has cultivated a brand that stands for more than just its products, earning trust and admiration from consumers and stakeholders alike.
These case studies illustrate the transformative power of aligning organizational culture with purpose. Whether through sustainability, inclusivity, or activism, these companies have proven that embedding values into operations creates not only strong business outcomes but also lasting societal impact.
VI. Challenges in Purpose-Driven Transformation
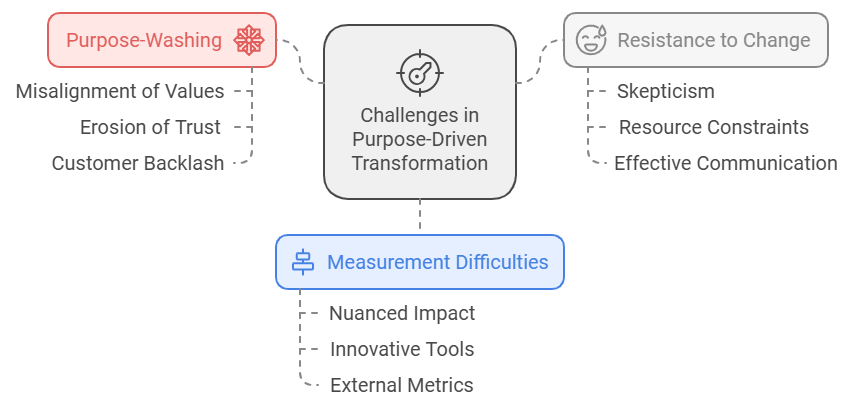
Embedding purpose into an organization’s culture is a powerful approach, but it comes with considerable challenges. One of the most pressing issues is the misalignment between an organization’s stated values and its actual behaviors, a phenomenon often referred to as “purpose-washing.” This occurs when companies make ambitious commitments to principles like sustainability or inclusivity but fail to reflect these values in their daily operations. Such discrepancies erode trust, leading employees to disengage if they perceive their organization’s mission as insincere. Customers, too, are increasingly vigilant, with social media and public discourse amplifying accountability. Brands that fail to deliver on their promises can face backlash, as seen in cases where organizations claim commitments to sustainability while engaging in environmentally harmful practices. To prevent purpose-washing, companies must ensure alignment between their values and actions, making transparency and consistent decision-making integral at all levels of the organization. Demonstrating authentic adherence to core principles is essential for maintaining credibility and trust among stakeholders.
Resistance to change poses another critical challenge in purpose-driven transformation. Realigning an organization’s culture requires shifts in behavior from employees and leaders, which can evoke skepticism and uncertainty. Employees may fear how new expectations will affect their roles or feel overwhelmed by the scope of cultural change. Leaders, meanwhile, may doubt the tangible benefits of prioritizing purpose, particularly when immediate results are not evident. Resource constraints, including limited time, budgets, or competing priorities, can exacerbate these concerns. Effective communication becomes crucial in addressing resistance. Leadership must clearly articulate the rationale behind the transformation and its potential long-term benefits for both individuals and the organization. Modeling purpose-driven behaviors is equally important, as it reinforces commitment and builds trust. Engaging employees in shaping the transformation fosters a sense of ownership, reducing resistance and fostering a collaborative approach to change.
Measuring the effectiveness of purpose-driven transformation introduces another layer of complexity. Unlike straightforward metrics such as revenue or market share, cultural alignment’s impact tends to be nuanced and long-term, making it harder to quantify. However, organizations that neglect measurement risk losing focus or overlooking opportunities for improvement. Innovative tools like Net Promoter Scores (NPS) offer valuable insights by gauging whether employees feel positively enough about their workplace to recommend it, serving as an indicator of engagement and satisfaction (Kaaria, 2024). Retention rates, diversity metrics, and employee survey feedback further illuminate shifts within an organization’s culture, enabling leaders to track progress and address areas requiring attention (Corritore, Goldberg, & Srivastava, 2020). Externally, metrics such as customer satisfaction scores and trust indices help measure the resonance of organizational values with stakeholders. For initiatives aimed at societal impact, tracking outcomes like reductions in environmental impact, community engagement, or charitable contributions provides a broader understanding of the organization’s success in aligning purpose with action.
Although the challenges of purpose-driven transformation—such as purpose-washing, resistance to change, and measurement difficulties—are significant, they are not insurmountable. Organizations that approach these obstacles with authentic intent, effective communication, and a commitment to strategic action can overcome them and realize the full potential of purpose-driven transformation. Success lies in acting consistently with stated values, engaging stakeholders meaningfully, and continuously refining strategies based on feedback. This ensures that purpose evolves from being an aspirational ideal to a deeply embedded reality within the organization’s culture.
VII. Measuring the Success of Purpose-Driven Transformation
Evaluating the impact of purpose-driven transformation requires a mix of quantitative and qualitative metrics. These measurements provide insight into how well an organization’s culture aligns with its values and mission, as well as the tangible outcomes of that alignment. Combining traditional performance indicators with narrative-driven assessments creates a comprehensive approach to understanding success.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Purpose-driven transformation often yields improvements in both workforce engagement and external stakeholder trust. The following KPIs can be used to measure these outcomes:
- Employee Retention Rates:
A culture aligned with purpose fosters loyalty, reducing turnover. Tracking changes in retention rates before and after implementing purpose-driven initiatives can reveal how effectively the organization is engaging its workforce. - Productivity Metrics:
Employees who feel connected to their organization’s mission are more likely to perform at higher levels. Productivity can be measured using output-per-employee ratios, task completion rates, or performance review scores, offering insight into how purpose influences day-to-day operations. - Brand Trust Scores and Consumer Loyalty Metrics:
External stakeholders often respond positively to companies that consistently live their values. Tools like customer satisfaction surveys, Net Promoter Scores (NPS), and trust indices can help gauge whether purpose resonates with the target audience. Metrics such as repeat purchase rates and customer lifetime value further reflect how loyalty is impacted by cultural alignment.
Storytelling as a Metric
Beyond hard numbers, storytelling provides a rich, qualitative lens for understanding the effectiveness of purpose-driven transformation. Capturing narratives from employees, customers, and other stakeholders highlights how the organization’s mission and values are perceived and embodied.
- Employee Stories:
Employees are powerful ambassadors for an organization’s culture. Collect stories that showcase how individuals live the company’s values, such as examples of collaboration, innovation, or community engagement. These narratives can provide context to quantitative data, illustrating the real-world impact of purpose-driven initiatives. - Customer Testimonials:
Purpose resonates strongly with customers when they see evidence of it in action. Gathering testimonials that highlight customer experiences aligned with the organization’s mission adds depth to metrics like satisfaction scores. For example, a customer sharing how they’ve been positively impacted by a company’s sustainability efforts can reinforce the brand’s authenticity. - Stakeholder Feedback:
Engage broader stakeholder groups, including partners, suppliers, and community members, to gather insights into how the organization’s purpose is perceived beyond its internal and consumer base. Their stories can help identify strengths and areas for growth in cultural alignment.
By combining measurable KPIs with the rich context provided by storytelling, organizations can gain a holistic understanding of the effectiveness of their purpose-driven transformation. This dual approach ensures that both the numbers and the human experiences behind them are considered, enabling organizations to refine their strategies and deepen the alignment between culture, values, and mission.
VIII. Conclusion
In a business environment defined by rapid change and heightened expectations, a culture aligned with organizational values and mission has become more than a desirable attribute—it is a strategic necessity. Organizations that authentically integrate purpose into their cultural fabric are better equipped to engage employees, foster innovation, and build trust with stakeholders. This alignment not only drives internal cohesion but also creates a strong foundation for navigating external challenges, ensuring long-term resilience and success.
As competition intensifies and workforce priorities evolve, businesses that fail to embrace purpose risk falling behind. Employees increasingly demand meaningful work that reflects their personal values, while customers are drawn to brands that demonstrate accountability and authenticity. Purpose-driven transformation offers a pathway to meet these expectations, creating a culture that resonates both within and beyond the organization.
Ultimately, embedding purpose authentically into every aspect of operations is not just about staying relevant—it is about thriving in a world where alignment between actions and values defines the leaders of tomorrow. By committing to this transformation, businesses position themselves to inspire loyalty, drive impact, and lead with integrity in an ever-evolving marketplace.
References
Corritore, M., Goldberg, A., & Srivastava, S. B. (2020, January–February). The new analytics of culture: What email, Slack, and Glassdoor reveal about your organization. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2020/01/the-new-analytics-of-culture
Edmondson, B. (2013). How Ben & Jerry’s brought maverick ideas to mainstream business. The Guardian. Retrieved from https://www.theguardian.com/sustainable-business/ben-jerrys-maverick-ideas-mainstream-business-values
Gartenberg, C., Prat, A., & Serafeim, G. (2019). Corporate purpose and financial performance. Organization Science, 30(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.2018.1230
Grant Thornton LLP, & Oxford Economics. (2019). Return on culture: Proving the connection between culture and profit. Grant Thornton LLP. Retrieved from https://www.oxfordeconomics.com/resource/return-on-culture-proving-the-connection-between-culture-and-profit
Harvard Business Review Analytics Services. (2016). The business case for purpose. Sponsored by EY. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from https://hbr.org/sponsored/2016/04/the-business-case-for-purpose
Harter, J. (2017). The right culture: Not just about employee satisfaction. Gallup. Retrieved from https://www.gallup.com/workplace/236366/right-culture-not-employee-satisfaction.aspx
Harter, J. (2023). In new workplace, U.S. employee engagement stagnates. Gallup. Retrieved from https://www.gallup.com/workplace/608675/new-workplace-employee-engagement-stagnates.aspx
Henderson, R. (2020). Reimagining capitalism in a world on fire. PublicAffairs.
Kaaria, A. (2024). Essential human resource metrics and analytics for sustainable work environments: Literature mapping and conceptual synthesis. East African Journal of Business and Economics, 7(1), 241–262. https://doi.org/10.37284/eajbe.7.1.1976
LeaderFactor. (2024, October 16). The importance of organizational culture in enterprise organizations. LeaderFactor. Retrieved from https://www.leaderfactor.com/learn/importance-of-organizational-culture
McKinsey & Company. (2020). Purpose: Shifting from why to how. McKinsey Quarterly. Retrieved from https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/people-and-organizational-performance/our-insights/purpose-shifting-from-why-to-how
O’Brien, D., Main, A., Kounkel, S., & Stephan, A. R. (2020). Purpose is everything: How brands that authentically lead with purpose are changing the nature of business today. Deloitte. Retrieved from https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/topics/marketing-and-sales-operations/global-marketing-trends/2020/purpose-driven-companies.html
O’Brien, I. M., Ouschan, R., Jarvis, W., & Soutar, G. N. (2020). Drivers and relationship benefits of customer willingness to engage in CSR initiatives. Journal of Service Theory and Practice, 30(1), 5–29. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSTP-08-2018-0186
Sundheim, D. (2023, December 12). How Patagonia became the most reputable brand in the United States. Forbes. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/dougsundheim/2023/12/12/how-patagonia-became-the-most-reputable-brand-in-the-united-states
Tabrizi, B. (2023, February 20). How Microsoft became innovative again. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2023/02/how-microsoft-became-innovative-again
Turner, J. (2023, March 29). Employees seek personal value and purpose at work. Be prepared to deliver. Gartner. Retrieved from https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/employees-seek-personal-value-and-purpose-at-work-be-prepared-to-deliver

2 thoughts on “Purpose-Driven Transformation: Aligning Organizational Culture with Values and Mission”
Comments are closed.